- 埃肯
- 可持续发展
- 政策、战略和报告
- 以前的报告和相关信息
- 2019 年可持续发展报告
- 2019年埃肯可持续发展报告
2019年埃肯可持续发展报告

埃肯简介和可持续发展报告
关于埃肯和埃肯的业务
埃肯成立于 1904 年,是非常注重环保的金属和材料制造公司,处于世界领军位置。
埃肯是一家完全一体化的生产商,业务遍及整个硅价值链,从石英到硅和下游有机硅特种产品,以及特种硅铁合金和碳素材料。
埃肯有 6,370 名员工,从事四个业务领域:有机硅、硅材料、铸造产品和碳素。公司总部设在奥斯陆,在全球拥有 31 个生产基地,有一个庞大的销售处和代理商网络,与客户密切联系,能进入具有吸引力的终端市场。
2018年埃肯在奥斯陆证券交易所再次上市。2019 年,埃肯的总营业收入为 226.68 亿挪威克朗,息税前利润为 26.56 亿挪威克朗。
愿景和价值观:
埃肯的愿景是“提供先进的硅、有机硅和碳素解决方案,为我们遍布全球的利益相关者创造价值,助力创建可持续的未来”。
我们的价值观是 尊重、参与、精准、持续改进。
有关 2019 年的完整财务报表, 请参见此处的年度报告。
2019 年埃肯的可持续发展报告
埃肯的使命是提供先进的有机硅、硅产品和碳素解决方案,助力建设更可持续的未来,为我们遍布全球的利益相关者创造价值。为了给利益相关者创造价值,埃肯努力打造负责任的环境足迹,确保经济增长的可持续性。同时,在公司责任范围内,埃肯努力成为积极正面和负责任的社会参与者。
根据与内部和外部利益相关者的对话内容,埃肯的可持续发展议程可分为四个领域。其中包括能源和环境、社会影响、有吸引力的雇主以及合规和治理。
2017 年,我们制定了一组可持续发展目标,使利益相关方能够通过年度报告来监控我们的进步。这些目标是基于以上四个重要领域而设立的,这些领域被视为埃肯的挑战,也是埃肯的机遇。因此,2019 年我们首次获得企业可持续发展评级公司 EcoVadis 的金级评价,感到非常振奋。
作为一家具有全球影响力的国际公司,埃肯欢迎民众对可持续发展的日益关注,并支持在这些问题上要保持透明度。埃肯将继续加大努力,以了解和改善组织的可持续发展足迹。
应对全球挑战的可持续解决方案:
对于埃肯来说,不断变化的环境既是一个机会,也是一项挑战。所谓机遇,是指市场对可再生能源、储能、交通解决方案、基础设施改善、数字化和医疗保健等的需求不断增长,而埃肯的产品是满足这些需求的诸多应用中的关键投入要素。
随着市场对低碳技术的需求继续增长,可预见的是市场对铁合金、硅和有机硅的需求也会不断增长,这就为埃肯提供了明显的机会。
所谓挑战,是指要生产风力涡轮机、太阳能电池板、电池、电动车辆和其他环保应用中所需的相同关键原材料,现有的技术仍不能令人满意。目前的生产技术一方面属于能量密集型,另一方面,又会大量排放二氧化碳。埃肯致力于在技术可行的范围内减少能源消耗和二氧化碳排放,并开发新技术,力求在生产中实现碳中和。
与利益相关方的接触
在整个价值链中,埃肯的运营活动对社会产生了重大的影响。埃肯的许多工厂都是当地社区的经济基石,对本地社区做出了重要的贡献,为本地社区提供安全的工作机会和基础设施,为当地缴付税款并支持当地社区发展。作为长期合作伙伴,埃肯重视与所有利益相关者(包括当地社区、政府和其他合作伙伴,如研究机构、客户客户和供应商)进行开放式对话。尊重是埃肯的核心价值观之一。我们与利益相关方的对话始终保持对个人、社会和环境的尊重。埃肯与各种利益相关者保持联系,有助于了解其在当地社区和整个社会中所扮演的角色,并建立长期的相互信任。
2019 年,我们继续开发利益相关者管理工具,以确保每个地点都有结构化的方法来确保利益相关者参与。我们计划在 2020 年使用该工具。有关我们与利益相关者的对话以及社区工作的更多信息,请访问第 80 页的社会影响章节。
埃肯的利益相关方:
- 员工
- 客户和供应商
- 地方和国家主管部门
- 企业管理团队
- 当地社区和组织
- 投资者和股东
- 工会
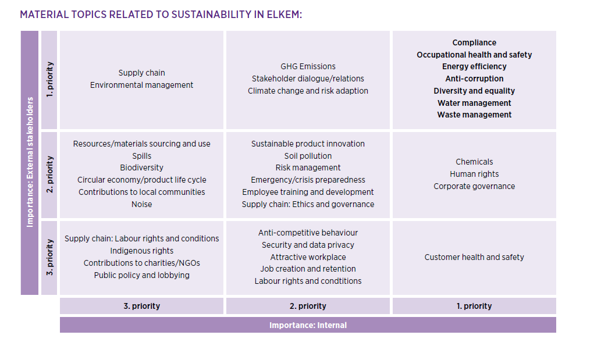
重要性评估
为了遵守全球报告倡议 (GRI) 以及 2018 年埃肯重新上市后产生的新利益相关者格局,集团去年与利益相关者进行了更广泛的互动和沟通。根据埃肯与内部和外部利益相关者的全面对话,重要性评估表凸显了埃肯在可持续发展中的优先事项。
在我们的重要性评估中,优先级最高的重要主题位于表格的右上角。我们的报告涵盖了这些主题。
政策和报告
埃肯的企业社会责任和可持续发展管理在以下政策中进行了定义:
- 埃肯的公司治理政策
- 埃肯的企业社会责任政策
- CSR指导委员会的授权
- 行为准则
- 举报政策
- 反腐败政策
- 竞争法合规政策
- 埃肯业务合作伙伴行为准则
埃肯的公司治理政策由董事会批准,规定了整体战略方法,而其他程序则由公司管理层批准。一个专门的企业社会责任(CSR)指导委员会负责发起和跟进公司的 CSR 工作。
埃肯的可持续发展报告是 CSR 报告的主要渠道,是根据 GRI 标准编制的:核心要求,并符合奥斯陆证券交易所关于企业责任报告指南中的规定。
为了维系投资者关系,我们还开发了一个有关埃肯关键 ESG 主题的指标(请参考相应的 ESG 报告)。该指标可在 www.elkem.com 上找到。
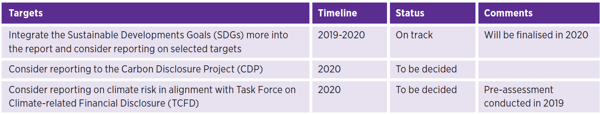
2017 年埃肯制定的可持续发展目标将于今年第二次公布。您可以在报告的每个章节中找到有关可持续发展的目标和进度。
报告目标
以下目标反映了埃肯如何在整体上管理可持续发展的行动和报告。本报告的每个章节都包括与我们的材料可持续发展主题相一致的具体目标。
承诺
埃肯致力于开展业务,以支持联合国可持续发展目标 (SDG) 和《巴黎协定》的愿景。作为联合国全球契约的成员,埃肯确保我们的业务符合联合国全球契约的十项原则。埃肯致力于遵守《联合国商业和人权指导原则》,并已发布《英国现代奴役法案》的更新声明。
埃肯遵守挪威公司治理委员会(以下简称 "NUES" 或 " 准则 ")发布的 " 挪威公司治理行为准则 " 的原则。本准则的目的是,在挪威受监管市场上市的公司实行公司治理,比法律要求更全面地规范股东、董事会和高级管理层之间的角色分工。
埃肯是全球负责任的关怀章程的成员,这是化工行业推动环境、健康、安全和安保改进的全球倡议。会员资格意味着承诺在整个生命周期内安全管理化学品。有关更多信息,请访问第 80 页的社会影响章节。
埃肯致力于遵守国际监管要求,并根据联合国全球统一化学品分类和标签体系(GHS)或其国家实施规定,提供其所有产品的安全数据表(SDS)。
能源和环境
目标和关键绩效指标
基于先进的生产技术,埃肯将自然资源转化为社会绝对依赖的产品。这需要大量的能源,对环境造成了影响——包括直接影响和间接影响。
将石英转化为硅是一种高温熔炼工艺,需要消耗大量能源。尽管埃肯生产的能源大部分是可再生能源,但也会对环境产生影响。生产过程本身使用化石煤、木炭和木屑等碳源作为化学转化还原剂,从而排放 二氧化碳、氮氧化物、二氧化硫和粉尘。二氧化碳的排放是这个工艺流程所固有的,使用当今技术无法完全消除。在埃肯的下游业务中,将硅转化为有机硅时还会对空气和水产生潜在的环境影响。
所有环境影响都通过测量或计算得到确认和记录,体现与埃肯运营所在地的政府当局规定的许可值和/或埃肯设定的改进目标等类似的结果。关键环境参数每季度在公司层面上报告一次。此外,还会及时报告、调查和密切跟进各种环境偏差。2019 年没有严重的环境事故。
由于潜在的环境影响,所有相关的埃肯工厂都必须拥有适当的环境管理系统,而且许多得到了ISO14001认证。此外,相关工厂必须拥有能源管理体系,有些工厂还需要通过 ISO50001 认证(请参见此处的认证列表 )。
环境战略
2018 年,埃肯更新了其环境战略,做出了以下承诺:
- 无论埃肯在世界何处运营,都完全遵守所有适用的环境法规。
- 无论埃肯在世界何处运营,都要树立并维护强大的环境声誉。
- 根据我们对生产环境影响的了解,确保可持续生产和废弃物排放控制。这也适用于相关环境法规较弱或不存在的国家 / 地区。
- 加强我们在技术和材料开发方面的地位,以减少全球温室气体的排放。
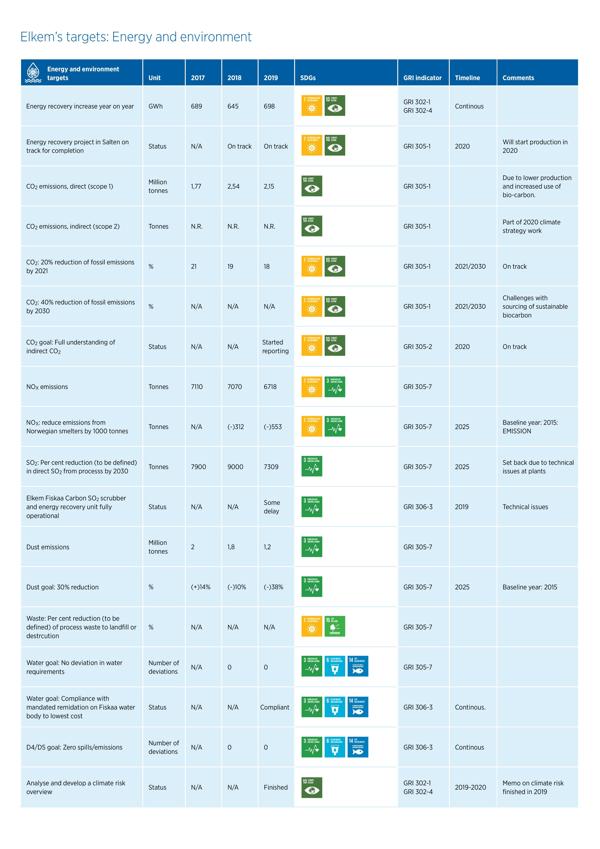
该战略引入了一套全面的关键绩效指标,包括每季度报告,涉及能耗、往大气和水体中排放的废弃物数量以及废物 / 过程产品。此外,还会在生产场所跟进其所制定的环境战略,并制定详细的路线图,显示如何实现目标。主要的环境关键绩效指标包括:

能源:消耗、回收和效率
能源:消耗量、回收率和效率
能源是确保必要供应的重中之重,同时也能减少全球温室气体排放。监管框架,例如特许权、指令、税、以公共支持形式出现的正面刺激等,更加强调了注重能效的重要性。
硅、硅铁和铸造合金都在电弧炉中生产,所以埃肯价值链的某些部分非常耗能。埃肯的熔炉每年消耗的电能接近 5 TWh。
埃肯是废热利用领域的工业先驱,在二十世纪七十年代已经安装了第一台用于熔炉的能量回收系统。冶炼炉回收的热量可以用作区域供热的热水、其他生产工艺的蒸汽以及产生新电能。电力被出售回电网,而热水和蒸汽可以在工厂内外使用,包括被用于为工厂附近的其他公司和社区供电。
能耗:
2019 年埃肯总耗电量为 6010 GWh,和2018 年的 6228 GWh 相比,有所下降。由于埃肯主要产品在全球的市场条件非常好,所以耗电量降低大部分是由于产量的降低。埃肯消耗的电力超过 83% 是基于可再生能源发电。除了中国的一家冶炼厂外,埃肯的所有熔炉均使用可再生电力。除了电能外,埃肯还消耗大约 1.4 TWh 的其他类型能源,用于内部车辆运行以及设施和流程的加热 / 冷却。其中大部分是基于化石燃料的能源。
能量回收:
作为气候计划的一部分,埃肯制定了长期战略,旨在逐年提高能源回收率。埃肯的许多生产过程产生的多余热量,通常是通过废气系统或冷却系统排放的。其中大部分可回收为区域供热热水,可提供给工厂内部和工厂附近的其他公共设施和行业,也可用作工业过程和 / 或发电所需的蒸汽。
所有冶炼厂的能源回收潜力均已确定。埃肯的三家冶炼厂已经将大型锅炉连接到废气系统,将大量能源回收为蒸汽或电力。2020 年,第四座工厂将投入运行,提供额外的 270 GWh 电力。2019 年,我们的工厂在全球共回收了 698 GWh 的热量和电力。与 2018 年相比,这相当于增加了 54 GWh。
能效:
所有埃肯工厂都需要拥有适当的能源管理系统和能源库存清单,以显示提高能源效率、节省能源的潜力。例如,用具有先进数字能源控制的新电机替换旧的低效电机。例如,请访问 www.elkem.com。
2019 年,埃肯在与基础设施和公用事业消耗相关的项目中节省能源 51 GWh,其中几项计划获得了公共支持。
二氧化碳排放、交易计划和其他空气排放
二氧化碳排放和碳交易计划
2019 年,埃肯从化石碳燃烧中排放了 215 万公吨二氧化碳,而 2018 年,这个数值为 254 万公吨。这主要是由于产量较低,但也因为熔炼过程中使用了更多的生物碳。在熔炉还原过程中,大约有 81% 的二氧化碳被直接排放,其中碳 (C) 与石英中的氧发生反应,生成了硅 / 硅铁。由于无法直接测量此类排放量,因此排放量是根据原材料中碳含量(TC)的第三方证书计算的。其他来源(包括供热和燃料)的二氧化碳排放量是基于符合欧盟排放交易体系(EU ETS)指南的标准转换系数而计算的。
由于二氧化碳 排放是当前技术下熔炼工艺不可避免的,因此每年的总排放量将根据市场条件和产能利用率而发生变化。由于二氧化碳的排放是当前技术下熔炼过程固有的,因此每年的总排放量随着市场条件和产能利用率的变化而变化。在过去几年中,埃肯集团的二氧化碳总排放量有所增加。所有这些都可能与扩大生产直接相关。自 2017 年起,埃肯新建了很多熔炉:挪威有两个,中国有四个,巴拉圭有一个。巴拉圭的熔炉用的是水力发电,其还原剂是生物碳,使其运营接近碳中和。二氧化碳的增加也与收购中国的上游有机硅工厂有关,该工厂使用煤燃锅炉生产所需的蒸汽。
埃肯正在开展一系列降低碳足迹的活动。这些活动基本上分为三个主要领域:提高材料和能源效率、用生物碳取代化石碳、开发新的碳中和熔炼技术。所有这些领域的进展示例详见 www.elkem.com。
埃肯的主要减碳战略之一是在我们的冶炼运营中用生物碳取代化石碳。我们的目标是:到 2021 年,将挪威冶炼厂的化石碳足迹减少 20%,到 2030 年减少 40%。2019年,埃肯集团已经提前实现了 2021年的目标,并继续与合作伙伴密切合作,以开发更高效、更环保的生物炭,用于硅和硅铁的生产。
交易计划:
我们的大多数冶炼厂都遵循欧盟排放交易体系及其外部修订方案(挪威和冰岛的工厂)的规定。作为欧盟体系的一部分,自 2013 年开始,埃肯每年平均获得 120 万免费配额,以避免生产线从欧洲转移到没有碳交易计划的其他国家 / 地区而发生碳泄漏。我们发现挪威的冶炼厂所分配的免费配额比欧洲其他国家少时,我们提出了申诉,增加了分配给挪威冶炼厂的免费配额。
其他排放到空气中的物质
埃肯同时排放氮氧化物、二氧化硫和粉尘。这些排放物主要来自碳煅烧工艺、硅 / 硅铁熔炼工艺和上游硅基产品工艺。排放量的变化与生产量的变化有关,但也可能受到原材料质量、过程控制和过滤系统投资的影响。
氮氧化物:
通过设备设计和工艺控制,埃肯不断减少氮氧化物的排放。2019 年的数据显示, 2018 年氮氧化物的排放量是 7,070 公吨,到了2019年,这个数值减少了大约 5%,降到了 6,718 公吨。
二氧化硫:
2019 年,埃肯排放了 7,309 公吨二氧化硫,而 2018 年这个数值为 9,000 公吨,降幅明显。由于埃肯主要产品在全球的市场条件非常好,所以大部分减排量是是由于产量的降低。对于如何减少二氧化硫的排放问题,传统上主要关注的是采购硫含量较低的原材料。由于这种潜力有限,因此在可行的情况下也在考虑使用净化系统。2018 年,埃肯碳(挪威)公司在挪威二氧化硫基金的支持下完成了大型二氧化硫过滤器的安装。遗憾的是,由于技术问题,该装置未按预期运行,事实上,在 2019 年大部分时间内都未运行。大多数技术问题现已解决,但要实现这项重大投资的全部预期效果还是面临着一些挑战。埃肯 Bjølvefossen 还在评估一个类似的项目。
粉尘:
埃肯分配了大量资源来控制粉尘。然而,极高的温度和快速分散的超细颗粒使捕获生产过程中产生的粉尘特别困难。
水和废物管理
水管理
从历史上看,埃肯的大多数生产设施都位于淡水供应充分且足以满足埃肯生产活动的地区,没有任何供水压力问题。水管理活动主要侧重于排放控制,以确保获得公共许可,使我们生产场所附近的水体得到适当保护,防止有害排放。随着埃肯在全球范围内扩张并越来越多地转移到化学加工领域,节水、现场回收和再利用已成为水管理计划的重要组成部分。
水是生产基础有机硅硅和中间体的重要原料,也广泛用于不同的加工步骤。埃肯的上游有机硅生产地点靠近法国和中国的重要淡水水体,化学品生产中的废水排放受到严格监管,这也增加了对水管理的关注。
几十年来,埃肯工厂一直根据适用的法规和许可证进行水体监测(淡水和海水)。在欧洲,这意味着遵守《欧盟水框架指令》,而其我们运营所在的世界其他地区则适用其他法规。埃肯生产过程中产生的三种主要污染物会对生产场所附近的水体产生负面影响;
- 在生产有机硅、硅铁和碳素产品的原材料中天然存在着一些重金属,可能会在生产过程中释放到空气中。雨水和地面径流会将这些金属带入到水体中。
- 碳素产品原料中发现的多环芳烃 (PAH) 成分对水生生物有害。这些废弃物进入水体的方式有两种:一种是直接排放工厂废水,另一种是排放到空气中的颗粒物被雨水带入水中,最终进入到海洋生物体内和沉积物中。适用的情况下,工厂会密切跟进这些废弃物的潜在和实际影响。
- 降低水体氧含量的有机物质,即化学耗氧 (COD) 物质,是有机硅生产过程所面临的主要挑战。应对这个挑战,对位于中国和法国的两个上游有机硅工厂尤为重要。
除了当前生产流程中产生的废水外,生产现场和周围的地面上也可能出现废水。埃肯的许多旧工厂位于有着上百年历史的工业生产区。多年来,我们的工厂一直建在垃圾填埋场上,并且 / 或者拥有自己的垃圾填埋场,因为这在当时的历史条件下是允许的。
我们密切关注所有这些历史排放和当前排放的情况,并在必要时使用有效的水处理设施将负面影响降低到可接受的水平。必要时还会实施和 / 或规划补救措施。
2019 年,埃肯的淡水总消耗量约为 8千万立方 米。其中大部分是在淡水供应充足、不存在水资源短缺情况的地区。然而,大约 10% 淡水消耗量来自南非和中国某些地区的淡水供应不足的地区。
废弃物处理
埃肯运营中践行零废弃物理念,这与埃肯业务系统 (EBS) 密切相关。其中的措施包括承诺在源头减少废弃物产生,在现场可行的情况下回收或再生副产品,并在交付给外部废弃物管理部门之前分离并回收任何剩余废弃物。
历史上,埃肯冶炼活动产生的废料主要由无害无机材料组成,如渣、产品颗粒、石英颗粒以及木屑和煤炭产生的少量有机颗粒。针对所有这些情况,我们已经启动了大量的项目,以回收和再利用废弃物而不是直接填埋。其中许多项目在创造新产品和更好地利用原材料方面取得了巨大成功(请参见 www.elkem.com)。
有机硅在不同生产工艺流程中产生的有机废物和有害废物的数量要高得多。危险废弃物的销毁由已认证的外部供应商管理,而其他废弃物则将根据当地法规进行焚烧或填埋。我们还启动了许多项目,以减少源头处的废弃物,并回收化学品以供重复使用,而不是销毁或沉积这些废弃物。
2019 年的废弃物填埋量为 340,000 公吨,其中包括已认证的第三方服务供应商所管理的 3,500 公吨危险废弃物。可用于自身生产或出售给其他人的副产品和耗材的回收量为 67,000 公吨。此外,136,000 公吨回收的熔炉粉尘被加工成微硅,这是一款具有多种用途的全价值产品,可以用于包括施工和建筑行业的混凝土加固。
环境偏差
2019 年未发生重大泄漏(定义为具有持久环境影响的泄漏)或重大环境事件。2019 年,埃肯在全球范围内共报告了 66 项环境偏差。其中大部分是埃肯在法国和中国的上游和中间体有机硅生产过程中出现的短暂许可偏差。
由于其位置靠近中国最大的淡水水体之一,埃肯星火有着非常严格的排水限制,因为水处理设施不能满足这些要求,2019 年期间政府对其进行了密切跟进。2019 年,为了满足排水的环保标准,还需要减少生产。
产品管理、关注物质和冲突材料
产品管理、关注物质和冲突材料
产品管理重点关注埃肯产品在集团客户储存、运输和使用过程中对环境、健康和安全的影响。这包括充分了解我们产品的潜在危险,并通过安全数据表和其他信息向客户和合作伙伴提供安全使用和处理的明确信息。
埃肯高度重视公司、部门和工厂级别的产品资源管理。
埃肯产品中的高度关注物质 (SVHC) :
埃肯有三个主要产品领域存在关注物质:
- 对于硅产品和铁合金而言,重金属是原材料中天然存在的元素。
- 对于碳素产品,煤焦油沥青高温在生产过程中用作中间体。
- 对于有机硅,D4 和 D5 在生产过程中生成为中间体,并用于生产下游有机硅产品。此外,在欧洲,生产过程中使用的一些添加剂被列为 SVHC。
硅产品和铁合金:
在生产埃肯的硅产品和铁合金时,会仔细选择天然原材料,以满足产品规范。天然原材料以及最终产品可能含有痕量的 " 关注元素 ",即重金属。然而,此类元素杂质的浓度低至几 ppm(百万分之几),因此远低于会引发监管行动的通用阈值 0.1%。埃肯的硅和铁合金产品目前没有故意添加 REACH 附录 XIV 列出的 SVHC。已对埃肯的产品进行了一系列的浸出试验,以评估关注元素的生物利用度。关键元素的浸出量很低,产品符合欧洲玩具使用(EN 71-3,玩具安全)或电子设备使用(RoHS 指令)规定,甚至符合德国联邦风险评估协会关于与食品接触的聚合物填料(BfR LII)的建议。
碳产品:
埃肯碳是全球最大的 Søderberg 电极膏制造商之一,用于全球金属生产。历史上,Søderberg 电极膏由煤焦油沥青和焦炭制成。使用高温煤焦油沥青需要得到欧洲 REACH 法规的许可。但是,由于在 Søderberg 电极中使用煤焦油沥青被视为中间材料,因此无需授权。埃肯碳已成功地用绿色替代品取代有害的沥青,现在可以提供越来越多的不含多环芳烃(PAH)的产品。这是埃肯和客户朝着无毒工作环境迈出的重要一步。
有机硅:
D4、D5 和 D6 是所有有机硅产品的关键中间体。在过去几年中,为了识别和验证这些产品的潜在危害,进行了广泛的研究和讨论,但世界各地的环境监管机构仍未对可能的环境影响达成共识。由于欧洲的最终环境分类仍在进行中,埃肯继续采取所有必要的步骤来降低任何环境风险(有关 D4、D5 和 D6 的更多信息,请访问 www.elkem.com)。
对于某些下游产品,某些定义为 SVHC 的酸和催化剂目前用于某些产品的配方。它们将受到严格控制,并尽可能进行替代。由于它们只是生产过程的一部分,不会对最终产品造成任何危害。
冲突材料:
冲突矿产是指来自世界特定地区的原材料或矿物,在该地区发生冲突并影响这些材料的开采和贸易。这些冲突矿物包括锡、钛、钨("3T")和金。埃肯在有机硅生产过程使用由这些物质制成的化学化合物,并实施严格的采购控制,确保这些物质的采购完全符合适用的欧洲法规。
危险品的安全运输:
全面分析与所有埃肯原材料和产品的运输、处理和存放相关的潜在危险,并记录确保安全执行的措施,并提供给物流供应商和客户。主要风险包括密封性失效,导致原材料和产品在运输过程中可能起火或释放有毒物质。为埃肯处理危险品的物流供应商经过严格筛选,并要求其拥有车辆和驾驶员的所有适用证书。在欧洲,不同的化学品生产商之间也有密切的合作,它们达成协议,在运输危险品的紧急情况下相互提供援助。
具有吸引力的雇主
目标
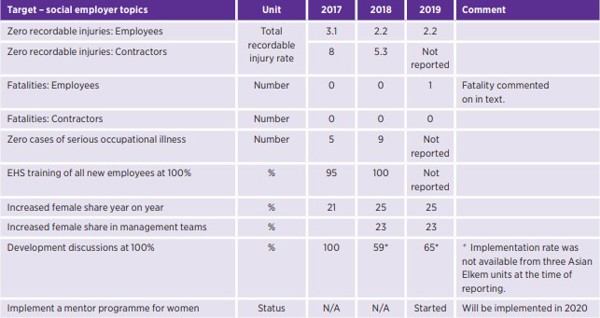
技术熟练、勤奋忠诚的员工是我们成功的基础,埃肯努力保持对员工的吸引力,既要留住已有的员工,又要吸引新员工。为此,我们的优先事项是健康和安全、培训和能力建设,以及促进平等和多样性。
环境、健康和安全 (EHS) 是公司业务的支柱,始终是我们的首要任务。我们在 EHS 方面的努力基于零伤害理念。我们员工的安全至关重要。我们坚信,并已在许多工厂证明,我们的生产不会对员工造成任何伤害。埃肯对埃肯企业和工厂中的所有活动负责,并确保在埃肯场所工作的员工和承包商员工也为自己的活动负责,避免造成任何伤害。
在强大的公司文化的支持下,我们致力于成为一个具有吸引力的、强调安全性的雇主,保护新老员工的利益。组织发展、持续的人才管理和系统性能力提升是公司发展和成功的关键,尤其是目前,我们公司正在快速成长。
共同文化:埃肯业务系统
埃肯在 29 个生产基地,拥有 6,370 多名员工,并在全球各地设有广泛的销售和行政办事处。
与所有组织一样,埃肯会与时俱进,公司文化也会随之发展。埃肯的价值观是参与、尊重、精准和持续改进。与埃肯业务系统 (EBS) 一起,这些价值观构成了埃肯公司的核心文化。EBS 是我们的业务理念、领导哲学和工具箱,为所有员工提供了共同的语言和工作方法,既推动企业的商业成功、也促进员工个人事业的发展。EBS 涵盖所有工作领域,包括生产力、质量和成本效益。EBS 的核心是让我们的员工参与改进工作,并赋予他们解决问题的能力。该理念的核心部分是埃肯各个层级的培训和能力发展项目。
埃肯在理解和控制往往不太稳定的工艺流程方面拥有丰富的专业知识。在上世纪 90 年代,让我们的工艺流程保持稳定的和可预测的运营状态是公司盈利能力的基石。如今,埃肯的工艺流程得到了更好的理解和优化,不过对员工的关注也与以往一样重要。只有人才能识别和解决问题。在这个过程中,他们将获得宝贵的经验、知识和个人发展。这就是为什么 2019 年埃肯决定将充分授权纳入到 EBS 标志的中心。一切都以我们的员工为中心。
开展EBS 评估,鼓励员工参与和持续改进
- 所有工厂均由企业 EBS 团队进行每年两次的评估,以衡量参与度和改进情况,并鼓励进一步发展。此外,我们也鼓励所有业务单位进行年度自我评估。
- 评估主题包括埃肯各个层级的学习活动、能力发展以及改进工作的结构 / 正式化。各单位应展示其员工队伍当前的知识和技能图表,并制定计划来填补任何能力差距,推动员工的进一步发展。
- 公司团队强调的重点是参与、知识和信息共享,是管理层应承诺建设共同的目标和工具,不断改进工作,为员工赋能。
多元化和平等性
多元化和平等性
埃肯是一家国际化公司,在世界各地的许多国家开展业务。拥有与这种全球强大业务相配的、具有多元化文化和个人背景的员工,是公司取得成功的必要条件。埃肯是特别关注当地人的利益,无论我们在哪里,都非常重视当地管理层和员工的价值。
埃肯致力于打造包容的环境,为所有员工提供平等的机会。我们认可并认识到,每个人都是独一无二,都是有价值的,他们的个人能力都应得到尊重。我们绝不接受基于性别、宗教、种族、国籍或民族、文化背景、社会团体、残疾、性取向、婚姻状况、年龄或政治观点的任何形式的骚扰或歧视。
我们非常重视平等性和多元化、公司价值观和行为准则。这些是埃肯入职培训课程 (EOP) 中的重要主题,也是所有新员工的强制性培训的一部分。埃肯的所有经理都应大力宣传多元化和平等性,多年来,多元化一直是埃肯领导力课程的关键主题。埃肯为全球一线经理提供了新领导力发展课程,其中包括多元化方面的培训。每位经理都必须遵循不歧视原则。
由于埃肯近年来在亚洲地区不断增长,我们已实施了若干举措,以确保亚洲地区开展有关我们的行为准则和非歧视原则的培训。我们合规部门的亚洲分支机构已根据当地业务环境调整了公司行为准则培训内容以及相关的道德困境。为确保所有员工完全理解并遵守行为准则,我们已为员工开设了培训课程。
为了进一步加强包容性和多元化的全球企业文化,埃肯于 2018 年启动了一项关于多元化和包容性的试点项目。2019 年,埃肯在营运所在的三个亚洲国家开办了多场研讨会。这些研讨会的重要议题包括解决不同形式的歧视、埃肯行为准则培训,以及讨论我们日常工作中可能出现的道德困境,提高员工的反歧视意识。2020年,我们将继续举办研讨会,为目标群体提供有关多元化和包容性的培训。
2019 年,我们大力宣传:对于具有多元背景的求职者而言,埃肯是具有吸引力的雇主,为此我们还开展了全面的工作,以审查现有实践的优劣。由此,我们采取了若干具体措施,例如为招聘经理们提供了有关多元化的培训并要求必须参加、表彰企业内多元化的典型案例,以及修订招聘广告和相关宣传材料的模板。
2019 年的相关事件:
2019 年,公司层面报告了一个与多元化和平等性相关的事件,该事件已根据公司程序进行了处理。该事件发生的部分原因是文化差异,最后我们对当事方进行了指导和培训来解决这个问题。
女性比例
埃肯重视性别多样性,并致力于每年实现更好的性别平衡。
加工行业通常男性居多。然而,由于自动化程度的提高,繁重的体力劳动减少了。我们高度关注环境、健康和安全,提供更好的工作环境,打造更可持续的运营。
2019 年,埃肯的女性比例为 25%,亚洲是女性员工比例最高的地区,为 28%。2017 年至 2018 年,女性比例显著增加,这是由于中国埃肯星火有机硅和埃肯永登硅材料工厂的加入,使得女性员工比例提高了。
2019 年,埃肯 24% 的领导者是女性。要提高女性领导者的比例,一个具体的行动是积极鼓励女性员工申请企业管理职位。埃肯的目标是参加埃肯领导力培训课程的参与者中,至少有 50% 应是女性。女性参与该课程的比例从 2018 年的 25% 增加到 2019 年的 32%。
过去几年,埃肯的女性比例一直保持稳定。我们已决定吸引和留住更多女性,尤其是在管理职位上。我们已经启动了几项专门针对女性员工的倡议。2019 年,我们建立了针对女性学员的导师计划试点项目,并将在 2020 年全年开展。该计划将在试点结束后进行评估并考虑全球推广。公司招聘政策和相关培训材料已更新,加入了每个招聘流程中都应有女性招聘人员和 / 或女性经理等主题,并在整个流程中跟踪女性求职者的比例。
董事会和管理层
埃肯董事会由来自德国、法国、中国和挪威的 11 名成员组成。董事会的女性比例为 36%。11 名董事会成员中有两名年龄在 30-50 岁之间。其余成员为51岁或以上。
埃肯的企业管理团队由十人组成,分别来自法国、挪威、中国和加拿大。管理团队由九名男性和一名女性组成。其中一名成员年龄在 30 至 50 岁之间,其余成员年龄在 51 岁或以上。
2018 年,埃肯开始对事业部和公司职能部门的男性管理团队的女性比例进行统计,以更好地了解女性比例并开始跟踪这个数据的变化。2019 年我们继续统计这个数据,不过没有将企业内的各种内部委员会包括在内。统计结果显示,向埃肯高层汇报的管理团队中,女性占比为 23%,与 2018 年相同。此外,统计结果也显示了组织内部的巨大差异。某些地方,女性占内部委员会和工厂管理层的 50%,其他地方的委员会或管理层根本没有女性。
2019 年,埃肯开始跟踪员工的年龄分布。跟踪结果表明,近三分之二的员工年龄在 30-50 岁之间。蓝领和白领员工的年龄分布与员工的总体年龄分布非常相似。
发展和培训
埃肯活跃于众多要求严苛的市场,始终需要持续发展和不断改进。埃肯的改进工作需要有针对性、速度要快、质量要高。埃肯积极利用员工的日常工作情境,将其作为学习的主要场所。我们相信,发展新技能的最佳方式是基于 EBS 原则,参与到实际改进工作和问题解决之中。我们还认为:承担新的责任是非常重要的学习和发展方式。为了加强我们的“做中学”的理念,我们还提供了一系列内部培训课程。
商定个人发展计划是埃肯所有员工应与其领导进行的年度讨论的内容。埃肯的全球目标是,所有职位和地点的所有员工应与其领导进行年度发展讨论,完成率应达到100%。
2019 年,65% 的埃肯员工进行了年度发展讨论。2018年,59% 的员工进行了此类讨论,两相比较,这个数值增幅明显。总体而言,76% 的埃肯单位实现了 90% 或更高的年度讨论完成率。2019 年65% 的埃肯工厂实现了 100% 的年度讨论完成率目标。2020 年,我们将加大努力,在整个组织内实现 100% 的年度讨论完成率目标。
离职率
员工离职率是吸引力的一个指标,说明了埃肯在留住员工方面的表现。2019 年,埃肯集团的员工总离职率为 8%。新员工中女性比例总计为 30%,离职员工中女性比例为 17%。这些数字表明,我们为吸引和留住女性员工所做的努力已经有了积极的成效。
集体谈判、承包商、童工和强迫劳动
埃肯完全支持员工的结社自由和集体谈判权。有了这些权利,员工可以与雇主一起推动变革,寻找解决方案,并在我们经营业务的一些国家(如挪威和法国)拥有悠久的传统和强大的地位。埃肯还在集体谈判协议和结社自由不太普遍的地区开展业务。我们的企业社会责任政策明确规定,在法律允许的范围内,所有员工都应获得有关结社权利和与管理层集体谈判权利的信息。这个话题对埃肯非常重要。
埃肯遵守我们运营所在国家 / 地区有关结社自由的当地法律要求。根据《挪威公司法》的规定,埃肯董事会中设有三个员工代表席位和两个员工观察员席位。
结社的级别因国家 / 地区而异。在某些国家 / 地区,员工是根据集体谈判协议进行组织和结社的。而在其他有些国家 / 地区,埃肯实体中没有工会。埃肯支持员工行使结社自由和集体谈判的权利,并与工会进行良好的合作。这也包括我们供应商的员工,合同协议中列出了相关条款。
2019 年,埃肯开始跟踪集体谈判协议 / 工会协议所覆盖的员工人数。总共有 61% 的员工受此类协议的约束,但不同的国家和地区存在明显差异。
童工和强迫劳动
埃肯在几个存在童工和强迫劳动风险的国家开展业务,例如亚洲、南美和非洲。我们非常认真地对待这一风险,我们绝不容忍在任何运营和设施中使用童工或强迫劳动。我们期望与我们开展业务的供应商和承包商也都保持相同的标准。
埃肯遵守《联合国商业和人权指导原则》,并承诺遵守《英国现代奴隶法案》。我们制定了明确的企业社会责任政策,来保护员工的权利,我们在所有新合同中加入了埃肯业务合作伙伴行为准则,以确保供应商的合规性。
我们了解,部分供应商的生产现场或我们自己工厂的工作风险性高,必须由受过培训且符合资格的成年人完成。
在埃肯工作的年龄限制是 18 岁,部分假期短工和高职学校学生的年龄限制可放宽到 16 岁。假期短工和职校学生只允许从事轻松简单的工作,这些工作被认为是安全的,不会与他们的学业相冲突。
为执行这些程序和我们的 CSR 政策,我们采取了若干措施。埃肯有严格的例行程序,确保所有官方许可和登记都符合当地法律,我们所有的员工都有书面雇佣合同、保险、纳税记录等。所有工厂都定期进行环境、健康和安全(EHS) 和企业社会责任( CSR) 审核,特别关注高风险区域的工厂。我们还举办了 CSR 研讨会,为员工提供知识和培训,提高员工的认识和技能。
埃肯的供应商受合同约束,必须禁止 15 岁以下儿童(部分特定国家/地区规定为 14 岁)在其工厂工作,并明确规定仅 18 岁以上的人员才能从事危险工作和夜间工作。我们依照合同规定,在批准新供应商之前会对供应商进行提前审核,对现有供应商进行定期审核,确保其符合以上这些标准。
2019 年的相关事件:
2019 年,埃肯或我们的供应商没有发生童工或强迫劳动事件。
承包商员工
承包商员工在埃肯的工厂和世界各地的其他工厂中提供各种服务,必须遵守与我们自己的员工相同的 EHS 要求。所有承包商员工都将接受全面的培训和跟进,以确保他们在安全健康的环境中工作。
2019 年,埃肯的承包商员工人数为 882 名,所谓承包商员工的定义是替代埃肯自己聘用的员工、为埃肯全职工作超过三个月的非埃肯员工。
社会影响
目标
埃肯相信,可持续发展是我们的核心责任,也是我们走在行业前沿并保持未来竞争力的先决条件。除了我们自己的运营外,埃肯还通过采购原材料、资本货物和服务,对社会、环境和经济产生显著影响。在向低碳社会过渡和减轻气候变化影响方面,加工行业发挥着重要的作用。
朝着更可持续的世界迈进,这个过程中蕴含的机遇和挑战是埃肯公司风险评估的一部分,分为市场风险、EHS 风险、企业社会责任风险和财务风险等相关领域。有关可持续发展风险的更多信息,请访问简介章节。
全球大趋势影响着我们的业务战略,并推动着埃肯的增长,这就要求我们专注于自己的运营,并将我们的产品和解决方案集中在满足未来的需求上。我们认为全球六大趋势对埃肯具有战略重要性,推动了市场对我们产品的需求:可持续性、能源需求的增长、快速城市化、生活水平的提高、人口老龄化和人口增长、数字化。
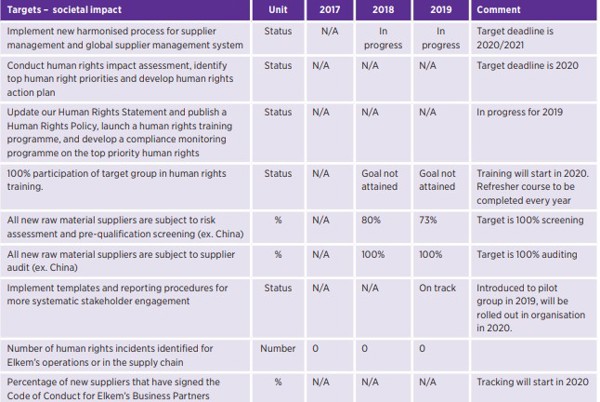
埃肯产品对可持续发展的影响
多年来,埃肯在可持续发展方面一直与多个客户进行密切对话。通过可持续发展评级公司 EcoVadis 的 CSR 评级等举措,我们能够跟踪我们在可持续发展方面的表现以及客户的期望。2019 年也是我们许多其他工作的里程碑,因为客户对我们产品的实际环境影响信息的需求显著增加。
埃肯支持这一发展,并与客户密切合作进行产品生命周期分析 (LCA) 。我们不断努力改善产品的环境足迹;降低二氧化碳和其他污染物(如氮氧化物、二氧化硫、粉尘和 PAH)的排放量。有关这些主题的更多信息,请参阅第 62 页的 " 能源和环境 " 章节。
埃肯还致力于改进排放量的计算和跟踪。埃肯有着零伤害的愿景,并努力为客户提供可持续的解决方案。目前,准备我们的产品组合将为我们带来未来的竞争优势,因为我们预计市场对 LCA 信息和环保产品的需求将增加。
埃肯的大部分二氧化碳排放都发生在硅和硅铁的生产工艺中。但是,我们的产品主要基于水力发电,因此与许多竞争产品相比,其环境足迹更小。平均而言,我们的硅生产中废弃物的排放量占全球平均排放量的三分之一,即每千克硅生成12 千克二氧化碳。
此外,在计算有机硅整个生命周期的温室气体排放时,硅材料的生产的温室气体排放量最大,因为其排放量占有机硅产品总排放量的 66%。
因此,由于不同地区的发电量不同,硅材料的来源地区对硅的二氧化碳排放量起着重要作用。在这里,埃肯的电力结构将成为计算 LCA 时的绿色比较优势。
埃肯为汽车行业提供产品。大型汽车公司在汽车开发过程中制定了评估和整合 LCA 的策略,这会影响我们的产品交付。埃肯硅材料公司正在努力评估和改善我们产品的二氧化碳足迹,并将继续成为汽车行业的环保产品供应商。
使用有机硅产品会有减排效应,与竞争对手的材料相比,减少了有机硅在生命周期结束时的环境影响。有机硅产品可实现更高效的运输,有助于减轻车辆重量,减少对加热能源和耗电量的需求,并有助于提高效率。有机硅的特性有助于延长材料寿命,确保更高效地使用材料,还可以取代油基塑料产品,降低材料生产和回收中的碳足迹。CES (欧洲有机硅中心) 于 2018 年发表的一项研究表明,在汽车、建筑和太阳能应用中使用硅的净效益最大,与替代方案相比,估计每使用一公斤有机硅,就会减少48公斤的二氧化碳等价物。
埃肯的产品监管
埃肯致力于确保安全处理、使用和处置我们的产品。产品监管是指在产品整个生命周期内主动地、负责任地管理产品的健康、安全和环境影响。
埃肯致力于遵守国际监管要求,并根据联合国全球统一化学品分类和标签制度(GHS)为所有产品提供安全数据表(SDS)。在推广埃肯产品的所有市场中,产品必须满足特定要求,并符合某些技术、监管、健康和环境标准。
这对我们的有机硅事业部尤为重要。积极管理化学品、保护环境、守护人类健康是开展业务和获得经营许可证的基本前提条件。产品注册、产品授权、安全数据表和产品标签等都必须符合化学品规范。埃肯还遵守一些行业特定法规,例如与食品和水接触的产品(包装)或医疗保健产品和服务(创可贴 / 伤口护理)相关的法律和法规。
除了遵守所有化学品生产法规外,有机硅事业部还签署了国际化学协会理事会(ICCA)的《责任关怀全球宪章》。产品监管是责任关怀计划的重要支柱,通过参与产品监管,我们将在产品的整个生命周期内都安全地管理化学品。其中包括,在我们整个运营过程中都会主动识别和管理化学风险和担忧,并替换产品组合中对人类健康、安全和环境构成不可接受风险的物质。
有机硅产品组合超过 4,000 种,广泛应用于多种情境中,因此遵守法规和产品合规性至关重要。我们已采用了OSCAR 文档管理系统,确保便于客户了解合规性规定、证书和监管声明。
我们的客户对其产品有自己的健康、安全和环境要求。埃肯的大多数安全数据表 (SDS) 可从 www.elkem.com 下载。由于要保护机密业务信息,某些选定产品的 SDS 仅可应要求提供。
社区参与和对话
当地社区的意见非常宝贵,有助于我们改进。我们与当地社区的对话中出现的关键话题包括社区发展项目、工作安全、安全运营、排放和其他环境问题以及工厂交通。当地社区提出的投诉以及与我们运营相关的交通事件均根据事故和偏差管理的良好实践进行登记和管理。有关埃肯处理外部投诉程序的更多信息,请参阅第 92 页的治理和合规章节。
与当地社区的对话由各工厂或现场经理负责,并以正式和非正式方式进行。工厂(或现场)经理有责任了解所有相关利益相关者,并在适用情况下与利益相关者进行对话(例如当工厂 / 现场发生变化时),并进行紧急培训。
ISO 9001 - 质量管理体系认证包括识别相关利益相关方并制定相关行动计划。此外,我们还为项目和工厂开发了自己的利益相关者工具。该工具于 2019 年试行,预计将于 2020 年实施。
当地社区支持:
一些埃肯工厂已经实施了本地倡议和支持计划。埃肯的社区支持包括提供更好的教育和当地基础设施、体育活动、减少当地社区贫困和食品支持以及其他社会影响倡议。
一些埃肯工厂已经实施了本地倡议和支持计划。我们的当地倡议和支持计划有着清晰的反腐败行动规范。任何财务支持均应根据当地法律以完全开放和透明的方式提供。当地工厂或单位应设定目标,评估当地社区计划的效果。
埃肯所支持的本地或地区性活动或计划示例:
- 当地体育俱乐部(儿童和成人)
- 奖学金(高中和大学)
- 专注于提升技能的学校课程
- 暑期学校 / 夏令营
- 癌症研究项目
- 向当地组织提供安全培训和急救箱
- 贫困家庭支持计划
2019 年,埃肯在挪威的社区活动开支为 521,000 挪威克朗。
2019 年,我们制定了一份通用的社区活动指南,以指导我们与当地社区的接触和互动。这个指南的目的是帮助我们工厂的当地决策者在与当地利益相关者互动时获得金钱或其他形式的支持。社区活动指南是基于《联合国全球契约》的原则,一旦实施,任何社区活动都应基于这些原则。这个指南将于 2020 年实施。
游说主张:
埃肯致力于为其所有业务获得令人满意的监管框架。在欧洲,这意味着需要分配足够的二氧化碳配额以及在电力价格中加上二氧化碳排放补偿费用。对挪威而言,埃肯的主张是寻求对工业电网电价方案进行持续修订,限制挪威与其他国家之间的输电线路的数量,因为向外输电,可能会提高国内电价。有关游说活动的信息,请访问 www.elkem.com。
负责任的采购和供应链
负责任的采购和供应链
该集团为其全球运营采购原材料、资本货物和服务。埃肯的总采购支出约为 160 亿挪威克朗,涵盖原材料、能源、商品、服务和物流的供应。活跃的供应基地由全球约 15,000 家供应商组成。
负责任的采购是埃肯的战略重点。负责任的采购意味着我们不仅仅从成本、质量和交货时间等传统方面来看待采购。这意味着埃肯致力于在所有购货类别和所有业务中采购产品和服务时考虑道德、劳工权利、社会和环境问题。
埃肯的采购:
公司供应链全面负责制定和维护埃肯的全球采购和物流战略,以及埃肯的全球采购政策和程序。
埃肯的采购组织是分散的,在公司层面、部门层面和工厂层面都有采购职能。我们对原材料采购和间接材料采购进行进一步区分。原材料供应商始终被视为关键供应商,间接材料供应商可能被视为关键供应商,具体取决于若干因素。
供应商尽职调查和根据环境和社会标准进行的筛选:
采购职能部门负责根据环境、健康和安全、社会责任、反腐败以及遵守法律法规等方面的公司要求,对供应商进行预评定和风险评估。
如果确定风险较高,则需要进行额外的尽职调查(诚信尽职调查)或现场审核。
2019 年,73%(中国除外)的新原材料供应商根据环境和社会标准进行了筛选。对于高风险供应商,进行了额外的尽职调查(诚信尽职调查)。一家供应商因尽职调查结果而被排除在外。
在 2020/2021 年,埃肯正在更新其供应商尽职调查流程,旨在采用统一的方法使用社会标准来筛查。所有新供应商都将根据 GRI 400 系列中的主题进行筛选。
供应商审核
原材料供应商的数量相对较少。制定了结构化审核计划,确保所有供应商都接受定期审核。
对于硬件、工厂设备和服务等商品和服务供应商而言,供应商数量很大。由工厂人员或公司人员进行定期审核,重点关注风险相关的供应。
埃肯负责任采购的相关政策包括:
- 埃肯供应商和业务合作伙伴的 EHS 和 CSR 批准:概述了埃肯的供应商预审和管理程序。
- 采购生物碳的企业标准:概述了埃肯对可持续森林管理的承诺,以及在埃肯采购生物基还原剂的要求。
埃肯业务合作伙伴的行为准则:
2019 年 10 月,埃肯发布了《埃肯业务合作伙伴行为准则》(以下简称 " 业务合作伙伴准则 ")。《业务合作伙伴准则》规定了埃肯对供应商在道德、劳工权利以及社会和环境问题方面的期望。
我们要求所有新供应商认可业务合作伙伴准则,并在整个关系中保持其承诺。业务合作伙伴准则被视为规范埃肯与供应商之间关系的任何协议的组成部分。
<strong>供应链中的EHS问题</strong>
埃肯为高风险供应商和承包商制定了针对采矿、运输、存储和装载等运营的健康、安全和环境标准以及详尽要求,并积极参与促进和监控为员工提供安全与合理的工作条件。其中包括健康和安全培训,并在必要时为供应商的员工提供适当的个人防护装备。同时还实施年龄控制,以防止童工的出现,并为年轻员工提供负责任的工作条件。埃肯要求供应商和承包商以公平的条款与其员工签订书面合同,并在法律允许的情况下向员工提供有关他们有结社自由和集体谈判权利的信息。
埃肯定期与供应商开会讨论这些规定。高风险供应商必须记录其对运营中的法律规范和潜在危险的理解,并制定计划,说明为埃肯工作时如何消除或控制风险。埃肯进行审计和检查,通常是日常访问以跟进质量、技术和业务,同时也有非预先通知的现场访问。外部审计员还会代表埃肯对供应商进行审计。
除了在必要时提出改进意见外,埃肯还会记录违反埃肯要求的行为,并通过口头或书面警告予以解决。反复违规的情况下,埃肯会要求快速执行改进计划、进行经济处罚或立即终止合同。
与 Achilles公司的战略合作伙伴关系:
2018 年,埃肯与供应链风险管理解决方案提供商 Achilles 合作。我们的许多挪威和冰岛供应商都在该公司进行了资格预审。Achilles 公司还每年进行 10,000 次审核。
持续改进:
埃肯是世界领先的硅基先进材料供应商之一,其运营贯穿石英到特种硅的整个价值链。在筛选供应商方面我们在不断改进。随着埃肯进入新兴市场,我们认识到需要优化、简化和数字化我们的供应链管理,为此我们开展了各种项目来提升我们的能力。
新的统一化的供应商管理流程:
2020/2021 年,埃肯将实施全球供应商管理体系,并引入新的统一化管理流程,用于供应商资格预审、供应链管理、供应链风险管理和合同管理。
这样,所有事业部和司法管辖区可以对供应商进行筛选和审查,在整个合同生命周期内跟踪和监控供应商的合规性,以及识别和管理供应商风险。
人权
埃肯的运营覆盖中国、马来西亚、韩国、印度、南非、俄罗斯、巴西、墨西哥和巴拉圭等具有挑战性的市场。人权问题通常深深植根于当地文化中,只有与利益相关者、政府和当地社区合作才能减轻这些问题。
埃肯严格遵守联合国商业和人权指导原则。我们还尊重并遵守《英国现代奴隶法》和《法国企业责任警戒法》的要求。
遵守这些原则,意味着埃肯必须识别和评估我们的运营和供应链中所存在的人权风险和影响。
埃肯的相关人权政策包括:
- 埃肯行为准则:我们尊重人权和劳工权利。
- 埃肯业务合作伙伴行为准则:我们的供应商应遵守全球人权原则。
- 企业社会责任政策:这个政策描述的是埃肯和社会企业责任 (CSR) 委员会如何保护人权和工人权利。
人权影响评估 (HRIA) :
我们的人权政策展现了我们对人权的承诺,解释了我们在埃肯和供应链中保护人权的方法。人权,尤其是工人权利,一直是埃肯的首要任务,也是我们 EHS 审计的重要组成部分。关于童工和强迫劳动政策的更多信息,请参见第 72 页的 " 有吸引力的雇主 " 章节。
随着我们不断发展并进入充满挑战的新市场,有必要对人权战略采取更系统化方法。因此,我们发起了人权影响评估 (HRIA) ,评估埃肯在整个价值链中的人权状况以及人权风险。
埃肯认识到人权在不断发展变化。因此,我们定期更新我们的影响评估,或在外部因素或埃肯的运营需要时更新人权信息,例如我们进入新市场、开发新产品或收购新业务实体时。
人权优先事项:
我们将根据人权影响评估( HRIA)的结果, 确定埃肯的人权优先事项,并启动人权行动计划。2020 年,我们还启动了人权培训课程,并制定了人权合规监测项目。
投诉机制:
根据《联合国商业和人权指导原则》,埃肯致力于纠正埃肯的活动造成或促成的人权被侵犯的情况。如果人权受到了影响,埃肯一定会彻底调查。因此,我们建立了一个外部举报渠道,允许匿名举报并与利益相关者联系。外部利益相关者可通过埃肯网站进行举报。
我们如何应对负面人权事件:
即使采用最佳实践,企业也可能造成或促成无法预见也无法预防的人权负面事件。在此类情况下,埃肯将尽一切努力防止或减轻影响:
- 如果埃肯造成不利的人权事件,我们会采取必要的步骤来阻止或防止其负面影响。
- 如果埃肯发生了负面的人权事件,我们会采取必要的步骤停止或阻止我们在其中的角色,并利用我们的能力来尽可能地纠正任何负面影响。只要我们有能力预防或减轻负面影响时,我们都会采取行动。
- 如果我们没有能力预防或阻止负面人权情况,我们将终止合作关系。
必要时,我们会向可靠独立专家进行外部咨询,包括政府、民间团体、国家人权机构和相关的多方利益相关者参与的倡议
治理和合规性
目标
埃肯认为良好的公司治理是创造价值、建立信任、获取资本的先决条件。为推行良好和可持续的公司治理模式,埃肯致力于在整个集团内建立良好和健康的商业实践、可靠的财务报告以及合规文化。
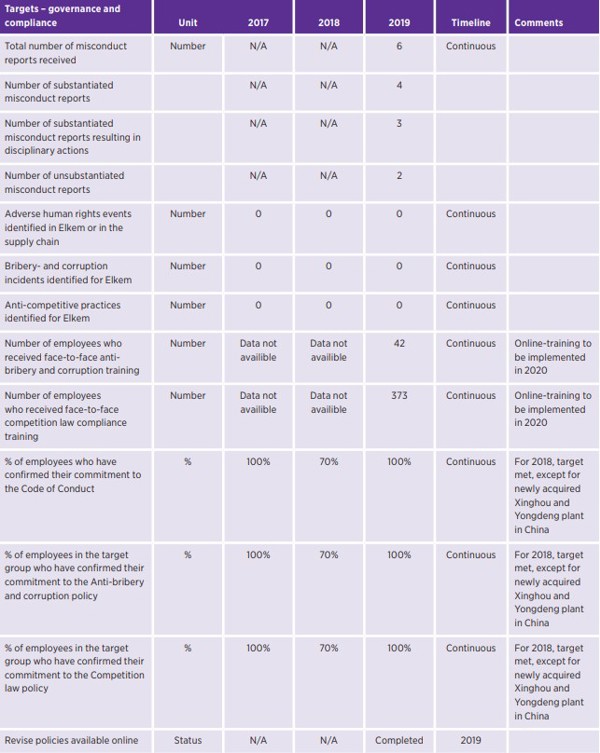
企业治理和合规性
企业治理
埃肯的企业治理框架在埃肯的公司治理政策中进行了概述,其中涵盖了审计委员会的说明、提名委员会的说明、薪酬委员会的说明、主要内幕人士的规则以及处理内幕信息的说明。本文件由董事会每年审查一次,上次修订日期为 2019 年 10 月 21 日。
遵守《挪威企业治理行为准则》(“NUES”或者“准则”)。本准则的原则反映在公司治理政策和所有其他治理文件中。
治理文件:
- 埃肯公司章程
- 企业治理政策
- 企业社会责任政策
- 全球行为准则
- 埃肯业务合作伙伴行为准则
- 举报政策
- 反贿赂和反腐败政策
- 竞争法合规政策
风险管理和内部控制:
董事会的最终责任是确保埃肯拥有健全且适当的内部控制系统和风险管理。为此,董事会每年对公司最重要的高风险领域及其内部控制安排进行审查。
运营管理层对直接评估、控制和降低风险以及确保充分的内部控制等方面有着最终的决策权,承担最终的责任和后果。管理层向董事会提供频繁且相关的运营和财务报告,确保董事会有足够的信息进行决策,并能够快速响应不断变化的情况。
企业帮助链,如 EHS、质量、产品责任、合规、企业社会责任 (CSR) 、法律、 IT、财务和其他控制部门,都会监督、促进和报告运营管理的风控活动。
由于埃肯在中国的营运规模及其风险,埃肯最近(2019 年)为亚洲设立了内部审计和合规职能部门。该职能部门向财务和会计副总裁汇报。
审计委员会:
审计委员会是董事会的子委员会,是有监管责任的董事会的准备机构,其工作任务是制作财务报告,确保公司内部控制系统的有效性。
如果对方要求,则首席财务官应与财务和会计副总裁和法律总顾问合作,向董事会审计委员会报告埃肯的内部控制和合规工作。
有关埃肯内部控制和风险管理系统的更多信息,请参阅 www.elkem.com 上的董事会报告和投资者关系页面。
合规
2019 年,埃肯聘请了一名企业合规官来领导公司的合规计划。公司合规官向总法律顾问汇报。
中国新任命的内部审计和合规职能部门可以在合规和人权问题方面,进一步支持企业合规工作。
2019 年成立的合规冠军网络:
公司合规由埃肯运营中的合规冠军网络提供支持。合规冠军是驻扎在各事业部的管理人员或支持职能部门的成员,协助公司合规职能部门实施埃肯的合规计划,包括为各个单位提供培训和指导。
企业社会责任委员会:
埃肯设有一个 CSR 委员会,由人力资源高级副总裁 (SVP) 领导,参与者来自合规、法律、 EHS、沟通、人力资源、采购和销售等关键职能部门。该委员会定期召开会议,其任务是培养一种企业文化,强调并设定企业社会责任的高标准,并根据这些标准审查企业绩效。人力资源高级副总裁负责向首席执行官报告 CSR 问题,并向董事会报告重大问题。
2020 年合规计划审核:
埃肯致力于持续改进。作为一项改进措施,埃肯将在 2020 年聘请外部顾问对合规计划进行独立评估。
举报渠道
在埃肯,开放性至关重要,如果出现问题,我们鼓励员工和利益相关者大胆发声。员工应随时与管理层讨论问题,或向人力资源或法务 / 合规部门举报不当行为,不会有被报复的风险。
用于举报外部不当行为的全球工具:
2019 年,埃肯推出了一个外部举报渠道,用于举报不当行为,并更新了公司的举报政策。举报渠道可供所有员工使用,并允许以埃肯所有语言进行匿名举报。本政策提供了有关举报方法的清晰指导。
我们的内部网站、埃肯网页、工厂和办公室的培训和实体海报和手册都提供了举报渠道和举报政策。
该渠道还可用作外部利益相关者(例如供应商、客户、埃肯运营所在的当地社区)的投诉机制。埃肯网站上有举报渠道和投诉方式,可以用多种语言举报或投诉。
不当行为举报后的处理方式:
有人举报不当行为后,由公司合规部根据适用的法规进行处理。任何对举报者的打击报复,埃肯都持零容忍的态度,并将对打击报复者进行惩罚。
培训
全球在线培训课程:
埃肯致力于提供最新、最相关且有吸引力的合规培训。2020 年,埃肯将推出一个新的全球在线培训课程,为所有员工提供相关在线学习内容,包括道德、反贿赂和反腐败以及反竞争等方面的培训。我们会定期更新培训内容,每年的培训内容都会有所不同。员工可以选择以埃肯的所有重要语言完成培训。
面对面风险培训:
在线培训之后,我们还为高风险司法管辖区和高风险员工群体提供面对面培训。我们的培训内容根据目标群体的特定风险和需求进行量身定制。
反竞争行为、反贿赂和反腐败
反竞争行为
埃肯致力于在所有运营中避免反竞争行为。竞争法合规政策概述了哪些行为被视为可接受或不可接受。
为改进预防措施,全面了解最易受影响的运营和员工群体,以及需要更新哪些反竞争实践。因此,我们正在进行反竞争行为风险评估,以识别高风险司法管辖区和员工群体,并识别危险信号和缩小差距。评估将于 2020 年到期。
反贿赂和反腐败
埃肯对腐败采取零容忍政策。埃肯在多个司法管辖区和几个高风险国家 / 地区开展多项业务。埃肯还处理政府官员的许可证和其他行政问题。
为了提高埃肯防止贿赂和腐败的内部控制和措施的效率,合规部正在对公司的全球运营进行反贿赂和风险评估(ABC 风险评估)。该评估将于 2020 年到期,并将成为未来反贿赂和反腐败计划的基础。2020 年评估将在进入新市场和引入新产品时定期更新。
与业务伙伴合作
对埃肯来说,与有高度道德操守的业务伙伴合作非常重要。埃肯不接受我们业务伙伴所进行的贿赂、破坏环境或侵犯人权的行为。在建立业务关系之前,关系经理必须对业务伙伴进行充分的尽职调查。在挪威和冰岛,供应商必须在Achilles公司 进行资格预审。
埃肯业务合作伙伴《行为准则》:
2019 年,埃肯推出了新的业务合作伙伴行为准则,建立在以全球行为准则、反腐败政策、企业社会责任政策和人权政策基础之上。所有新供应商都必须同意遵守并签署本准则,才能成为埃肯的业务合作伙伴。
第三方风险管理程序:
贿赂案例、侵犯人权、环境灾难和 EHS 事件通常涉及业务合作伙伴,如代理商、顾问、供应商、合资合作伙伴和分销商。为了确保我们以高效的方式处理与此类业务合作伙伴相关的风险,埃肯正在推出第三方风险管理系统 (TPRM) 。该系统将对所有业务方进行风险评估,筛查制裁名单和负面媒体,以及在其整个生命周期内对业务合作伙伴进行基于风险的尽职调查、审计和监控。该系统预计将于 2020/2021 年实施。